What is Cord Tissue?
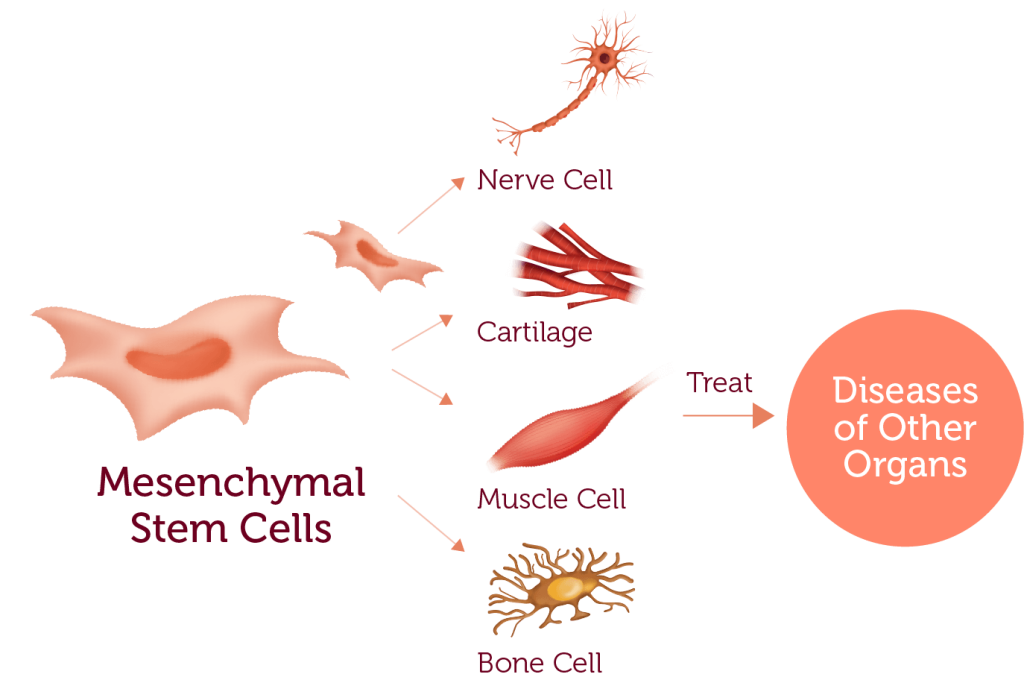
Cord tissue is the structural material of the umbilical cord, containing a unique type of stem cell called mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).
MSCs have different capabilities than the hematopoietic stem cells from cord blood. They can rapidly divide and regenerate a variety of different cell types in our bodies, like muscles, nerves and cartilage.
How is Cord Tissue Collected?
Collecting cord tissue is a simple process that occurs right after birth. Once the umbilical cord is cut, your healthcare provider will collect a small segment and place it in a special container.
This procedure is safe, painless, and does not interfere with the birth process or bonding time with the new baby. Instead of being discarded, the cord tissue is preserved, offering a valuable source of stem cells for potential future use.
Benefits of Banking Cord Tissue
Rich in Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Potential for Regenerative Medicine
Extended Treatment Possibilities
Guaranteed Match for Your Child
Benefits Extend to Family
A Lifetime of Possibilities
What parents are Saying



Ready to explore our banking plans?
What is Cord Tissue?
How is Cord Tissue Collected?
When you choose to preserve your newborn’s cord tissue, your delivering healthcare provider will cut a segment of the umbilical cord and place the umbilical cord in a provided collection vessel.
Banking cord tissue does not impact your birthing process. It is a quick and painless procedure that will provide your child and your entire family with lifetime access to a valuable source of stem cells.
Clinical Trials Exploring Future Potential
More than 1000 clinical trials are currently looking at using both cord blood and cord tissue stem cells as possible therapeutics. Hematopoietic stem cells from cord blood are being investigated for the use in treatment of diabetes, stroke and autism spectrum disorder. Additional clinical trials are examining the use of mesenchymal stem cells from cord tissue for treating osteoporosis, arthritis and brain injuries.
With the amazing progress being made in stem cell research, the list of diseases that can be targeted with cord blood and cord tissue stem cells in the future will continue to expand. It is highly like that many highly prevalent diseases of today such as diabetes, heart disease and Alzheimer's will be treated with cell therapies in the lifetime of your child.
Explore Clinical Trials
| LEUKEMIA | OTHER BLOOD CANCERS | METABOLIC DISORDERS | IMMUNE SYSTEM DISORDERS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Biphenotypic Leukemia | Acute Myelofibrosis | Adrenoleukodystrophy | Ataxia-Telangiectasia |
| Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia | Agnogenic Myeloid Metaplasia | Beta-Glucuronidase Deficiency | Kostmann Syndrome |
| Acute Myelogenous Leukemia | Essential Thrombocythemia | Gaucher Disease | DiGeorge Syndrome |
| Acute Undifferentiated Leukemia | Hodgkin’s Disease | Hunter Syndrome | Bare Lymphocyte Syndrome |
| Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia | Multiple Myeloma | Hurler Syndrome | Omenn Syndrome |
| Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia | Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma | Krabbe Disease | Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency |
| Juvenile Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia | Polycythemia Vera | Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome | Severe Combined Immunodeficiency |
| Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia | Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia | Maroteaux-Lamy Syndrome | Common Variable Immunodeficiency |
| Plasma Cell Leukemia | Metachromatic Leukodystrophy | Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome | |
| Morquio Syndrome | X-Linked Lymphoproliferative Syndrome | ||
| Mucolipidosis II | |||
| Mucopolysaccharidoses | |||
| Niemann-Pick Disease | |||
| Osteoporosis | |||
| Sanfilippo Syndrome | |||
| Scheie Syndrome | |||
| Sly Syndrome | |||
| Wolman Disease |
| RED BLOOD CELL DISORDERS | PHAGOCYTE DISORDERS | OTHER MALIGNANCIES | PLATELET DISORDERS | HISTIOCYTIC DISORDERS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aplastic Anemia | Chediak-Higashi Syndrome | Neuroblastoma | Amegakaryocytosis | Familial Erythrophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis |
| Beta Thalassemia Major | Chronic Granulomatous Disease | Renal Cell Carcinoma | Amegakaryocytosis | Histiocytosis-X |
| Fanconi Anemia | Neutrophil Actin Deficiency | Retinoblastoma | Hemophagocytosis | |
| Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria | Reticular Dysgenesis | |||
| Pure Red Cell Aplasia | ||||
| Sickle Cell Disease |

