Duration
5:30 minutes
Category
Stem cell basics
Series
Cord blood banking
Objective
Educational
Stem cell therapy explained
What you will learn
- What is stem cell therapy?
- Allogenic and autologous transplants
- Sources of stem cells
- How allogeneic transplants work
- Potential drawbacks of allogeneic transplants
This lesson aims to acquaint you with the functioning of stem cell therapy, its potential drawbacks, and the existing reservoirs of stem cells.
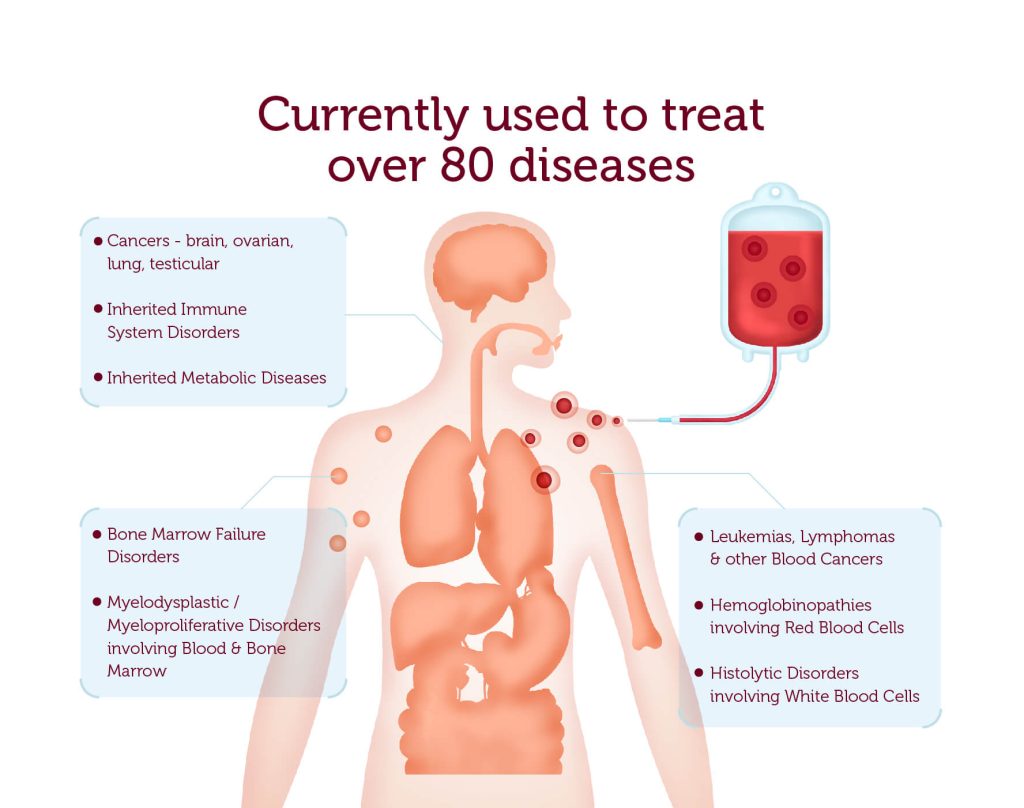 Stem cell therapy encompasses the application of stem cells to address and prevent diseases. For more than six decades, hematopoietic stem cells have been harnessed to manage blood disorders and immune system ailments.
Stem cell therapy encompasses the application of stem cells to address and prevent diseases. For more than six decades, hematopoietic stem cells have been harnessed to manage blood disorders and immune system ailments.
Hematopoietic stem cells serve as the progenitors of other blood and immune cells within our bodies.
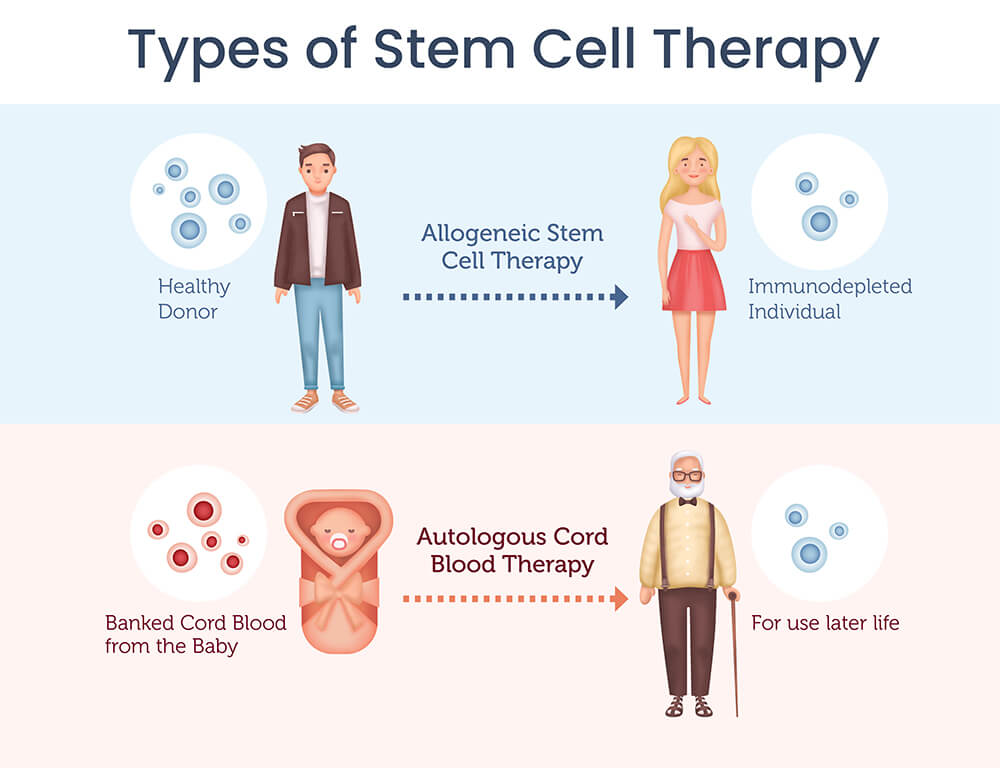
Presently, hematopoietic stem cell therapies are broadly classified into two categories: allogeneic and autologous therapies.
Allogeneic stem cell therapy involves acquiring healthy stem cells from a donor and introducing them into a patient for treatment.
Autologous stem cell therapy, on the other hand, involves substituting a patient’s impaired stem cells with their own healthy stem cells.
 For example, in cancer treatment, autologous transplants entail the collection of healthy stem cells from a patient before undergoing chemotherapy.
For example, in cancer treatment, autologous transplants entail the collection of healthy stem cells from a patient before undergoing chemotherapy.
Post-chemotherapy, these healthy stem cells replace the damaged ones within the patient’s body.
A 2012 survey conducted by the Worldwide Network for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Group revealed that approximately 47% of hematopoietic stem cell transplants were allogeneic. Finding a compatible donor is a prerequisite for patient treatment, an often intricate task.
In allogeneic transplants, the initial stages involve procuring stem cell samples from a donor, typically through a blood sample or, in a majority of cases, a bone marrow sample.
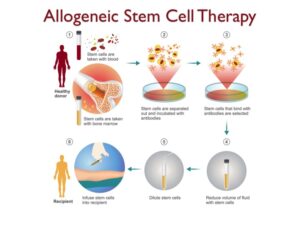
The ensuing step entails the purification of stem cells from these samples using specialized antibodies. The selected stem cells undergo further processing before being transplanted or infused into the patient.
Nonetheless, allogeneic stem cell therapy is not without limitations.
Primarily, finding a matching donor can be exceptionally challenging.
Even with a compatible sample, there’s a notable risk of rejection due to graft versus host disease. This occurs when the patient’s immune system identifies the transplanted cells as foreign and initiates an attack. Furthermore, bone marrow donation necessitates surgery, making it an invasive procedure even for the donor.

Lastly, the age of the donor can impact the process, as stem cells also age. Studies have revealed significant differences in robustness between stem cells from young and older donors. To delve deeper into this subject, refer to our lesson on stem cells and aging.
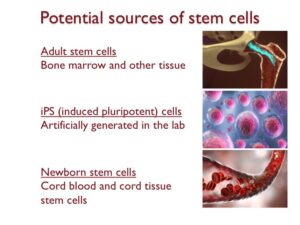
This lesson concludes by spotlighting potential sources of stem cells for cellular therapies: adult stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS), and newborn stem cells.
Adult stem cells can be extracted from bone marrow and various other tissues. However, their isolation can be challenging due to a decline in stem cell numbers as we age.
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) are a prominent focus of laboratory research. These stem cells are engineered in labs by reverting adult cells to their pluripotent state.
While iPS cells have driven breakthroughs in stem cell research, their safety and effectiveness for cellular therapy remain to be solidified.
Newborn stem cells are sourced from cord blood and cord tissue. However, the primary limitation lies in the fact that these stem cells can only be collected during birth.
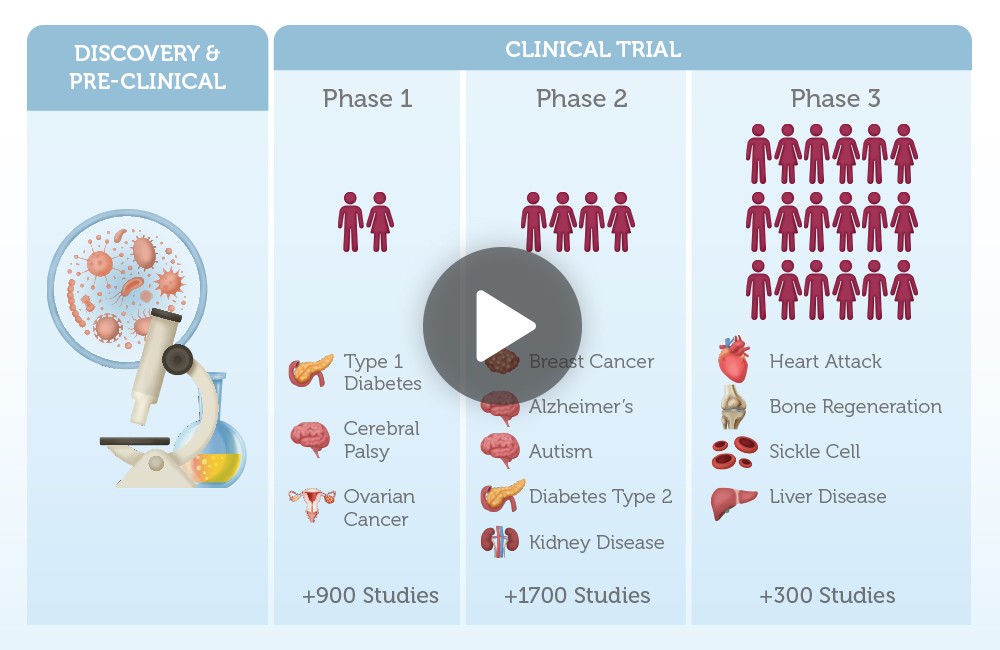
Across the globe, numerous clinical trials are exploring the potential of stem cell therapy in treating prevalent conditions such as diabetes, Alzheimer’s, osteoporosis, and arthritis. By preserving newborn stem cells today, you offer your child the prospect of accessing these potentially transformative stem cell therapies that might emerge in their lifetime.
More topics you might like
Continue your journey by selecting another topic.
What are newborn stem cells and why are they important?
3:45 minutes | Stem cell basics
Discover more about the placenta, cord blood and cord tissue.
4:00 minutes | Stem cell basics
Learn about the exciting new ways stem cells are being explored as a future therapeutic.
5 minutes | Stem cell basics